Section II: Prevention
Chapter 4 – Cancer Preventers
In the previous section, we described the cancer process and discussed several topics related to actually having cancer (what it is, how you get it, symptoms, detection, etc). From here on, we stick to the concept of preventing it.
There are several proactive actions you can take to prevent cancer. Any one of them will reduce your chances of developing it, but if you follow all, or at least most, of them you will be so well protected that it will be very difficult for you to get it. As we have mentioned before, the factor that most determines your susceptibility to cancer is your diet. Hence, ensuring that you get the right nutrients into your body is the most important part of any cancer prevention program. The next thing is to avoid as many carcinogens as you can (see the list in the previous section). Last but not least is exercise, which we discuss at the end of the section.
In this section, we describe the many foods and substances that help prevent cancer. We do not give many recommendations here because we have an entire section that gives specific recommendations for each preventer, including dosage, what foods it is found in, how to get the most out of it, precautions, and other important information.
Nature has the answers
It has often been said that nature has the solutions to all our problems. Every day there is additional evidence that validates this theory. Every day a scientist discovers a new naturally-occurring substance that helps heal some illness or that improves our health in a meaningful way. We address much of the research that has produced positive results regarding the use of natural substances that have anti-cancer properties.
Cancer and other degenerative, chronic diseases for which there are no cures have been outsmarting researchers at pharmaceutical companies for decades. It is highly doubtful that a "synthetic" or chemical cure for cancer will ever be developed. What pharmaceutical companies do is try to extract some tiny part of a natural product, modify it in a patentable way, package it, and expect it to fight a very complex disease in a very complex organism (your body).
Most natural compounds that prevent disease or cure it work best when used in their natural state, in other words when ingested as part of the whole food they come from. It is no coincidence that people that eat lots of fruits and vegetables are usually the healthiest individuals. These people are the ones that usually don't get cancer – they are attacking it before it gets to them.
Nature has the answer to many important problems in the world, and cancer is no different. We believe that one day scientists will say to themselves, "It was in front of our noses all the time. We couldn't see the forest for the trees." They will say this because it will probably be naturally-occurring compounds that hold the final solution to this deadly disease. Notwithstanding, it will become quite clear as you read on that nature can already protect you from cancer if you know what to eat and which natural supplements to take.
Antioxidants
Antioxidants are found in most fruits and vegetables. Some of them have more of certain antioxidants than others, but they are basically all found in nature's bounty. Most, if not all, antioxidants are good for your health in one way or another. One reason it is important to get a good, balanced mix of the different kinds of antioxidants is that some work better against certain free radicals than others. The other reason is that many of them help each other out. Some boost the effectiveness of others, replenish them, recycle them, prevent them from getting oxidized themselves, or increase their bioavailable levels.
It is also important to note that, although we recommend many different antioxidant supplements, you should do your best to get as much of each one from its original source, namely the fruits and vegetables that they come from. The reason for this is that there are probably other substances in the fruits and vegetables that enhance the power of the antioxidants or that have other cancer-preventing properties.
Many studies have found that people with cancer have low amounts of certain key antioxidants in their blood or in the particular organ where the cancer has developed. This is either because the person had low amounts of the antioxidants, which led to the cancer, or because cancer consumes antioxidants. Many cancers consume small amounts of certain antioxidants, meaning that it is easier for the cancer to spread once it has already started because the body will lack the antioxidants it needs to combat the cancer or other diseases that might result from a weakened immune system. A recent study at the University of Washington found that mice that were genetically engineered to produce extra amounts of a human antioxidant (catalase) lived approximately 20 percent longer than normal mice. It is widely believed that natural antioxidants from fruits and vegetables provide similar benefits to human beings.
Furthermore, studies have shown that large amounts of antioxidants can be harmful to cancer cells. Certain antioxidants have been found to induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) in tumor cells while leaving normal cells unaffected. Others have been found to lead to cell differentiation (i.e., turning a malignant cell into a normal cell) or growth inhibition in cancer cells. These are some of the many reasons to get your fair share of antioxidants in order to prevent cancer or to limit it once it starts.
In the following chapters we sometimes mention how much stronger of an antioxidant certain substances are than vitamins C and E. Although certain antioxidants might be "stronger" than others, this does not mean that they are better per se. Even though many of the antioxidants described in this book are "stronger" than vitamin C and E, this does not necessarily mean that they are better at preventing cancer, but rather that they are better at cleaning up certain free radicals, which is a good thing but not the most important one.
About vitamins
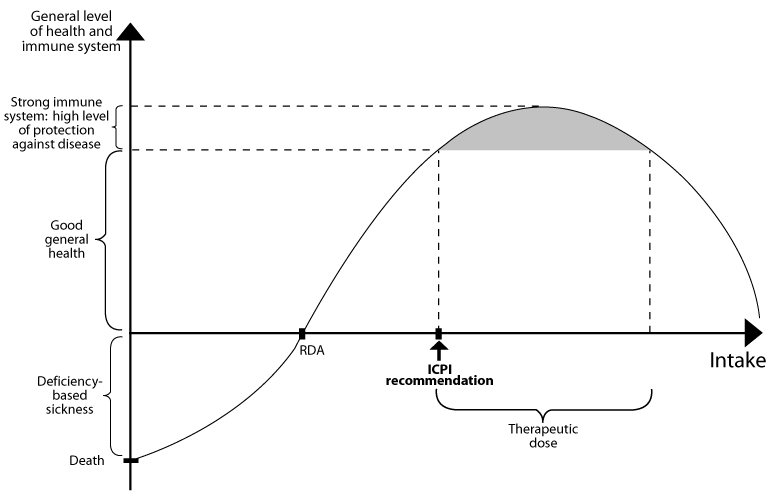
Vitamins are organic molecules that, among other things, function as catalysts for chemical reactions within our body. If you have a vitamin deficiency, you are missing catalysts, which leads to a breakdown in normal bodily functions and leaves the body susceptible to disease. Most people, including many doctors, think that we only need the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for each vitamin. However, most cancer researchers and other scientists, including the Institute, know otherwise. The RDA was established to make sure our bodies can perform our basic bodily functions. For practically all vitamins, you need much more than the RDA to protect yourself from cancer and other degenerative diseases.
Despite the fact that most people need higher amounts of most vitamins, there are toxic levels. Hence, even though most of us should probably take more vitamins than we currently take, there are limits that must be carefully observed. Every vitamin has an upper limit, which, if exceeded, can lead to medical problems or in rare, extreme cases even death. For most of the vitamins discussed below, we recommend doses that are therapeutic, but which are well below the toxic levels. We also tell you what the toxicity levels are for many of the vitamins we recommend. Figure 2 describes our needs for vitamins, minerals and other essential nutrients.
Figure 2: Essential Nutrient Doses
10